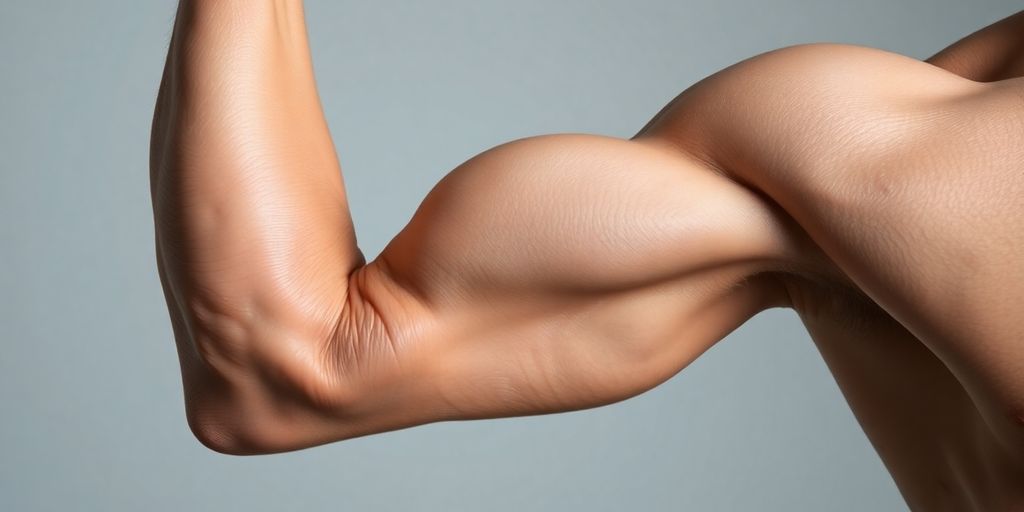
When it comes to muscle performance, understanding the concept of tension passive is key. This term refers to the resistance muscles provide when they are stretched beyond their normal length. It's different from active tension, which comes from muscle contractions. In this article, we will explore how muscle length affects performance, the role of tension passive, and why it's important for fitness and training. By breaking down these concepts, we can better appreciate how our muscles work and how to optimize our workouts.
Key Takeaways
- Tension passive is the resistance muscles exhibit when stretched, which differs from active tension generated during contractions.
- Muscle length plays a crucial role in determining how much force a muscle can produce, with an optimal length for maximum tension.
- Overstretching can lead to injuries and decreased performance, emphasizing the need for proper stretching techniques.
- Incorporating tension passive into workouts can enhance flexibility and strength, making training more effective.
- Understanding tension passive helps debunk common myths about stretching and muscle performance.
Exploring The Basics Of Tension Passive
What Is Tension Passive?
Tension passive? It's a term you might hear thrown around in fitness circles, but what does it really mean? Well, simply put, it's the tension that develops in a muscle when it's stretched, even when you're not actively contracting it. Think of it like a rubber band – the more you stretch it, the more resistance you feel. This resistance is tension passive in action. It's all about the muscle's inherent properties, not your conscious effort.
How Does It Differ From Active Tension?
Okay, so we know what tension passive is, but how's it different from active tension? Active tension is what happens when your brain tells your muscles to contract. It's the force you generate when you're lifting weights, running, or even just flexing your bicep. Active tension relies on the interaction of actin and myosin filaments within muscle fibers. On the other hand, passive tension comes from the muscle's connective tissues and titin filaments being stretched. It's like the difference between revving an engine (active) and stretching a spring (passive).
The Role Of Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is the unsung hero of tension passive. It's the stuff that holds your muscles together, providing structure and support. Think of it as the scaffolding of your muscles. This tissue, made up of things like collagen and elastin, resists stretching, contributing significantly to passive tension. The amount of connective tissue varies from muscle to muscle, which is why some muscles feel tighter than others. It's also why older muscles tend to feel stiffer – connective tissue becomes less pliable with age. So, next time you're stretching, remember to thank your connective tissue for the assist!
Understanding the role of connective tissue is key to appreciating how muscles behave under different conditions. It's not just about the muscle fibers themselves; it's about the whole package working together.
Here's a quick rundown:
- Connective tissue provides structural support.
- It contributes to the muscle's resistance to stretch.
- Its properties change with age and activity level.
The Science Behind Muscle Length

Understanding Sarcomere Length
Okay, so let's talk sarcomeres. These are the basic units within our muscle fibers, and their length is super important. Think of them like tiny engines that drive muscle contraction. When we talk about muscle length, we're often really talking about the average length of all those sarcomeres lined up in a row. It's not just about how long the whole muscle is, but how stretched or compressed these little guys are. This all affects how well the muscle can do its job. It's like, if the engine parts aren't aligned just right, the whole thing sputters, right?
The Length-Tension Relationship Explained
This is where things get interesting! The length-tension relationship basically says that there's an ideal length where a muscle can generate the most force. Too short, and the filaments inside the sarcomere get all bunched up, and they can't grab onto each other properly. Too long, and they're too far apart to make a good connection. It's like trying to high-five someone when you're both too close or too far away – you just can't get a good smack! Understanding this relationship is key to understanding how muscles perform. The length-tension relationship in muscles is crucial for optimal function.
Factors Influencing Muscle Length
So, what affects muscle length? Lots of things! Genetics play a role, of course. Some people are just naturally more flexible than others. But lifestyle factors are huge too. Think about:
- Posture: Slouching all day can shorten certain muscles.
- Activity Level: Regular stretching and exercise can help maintain optimal muscle length.
- Injuries: Scar tissue from injuries can limit muscle flexibility.
Keeping your muscles in a healthy range of motion is important. It's not just about being flexible, it's about making sure your muscles can do their job effectively and without getting hurt. Think of it as maintaining your car – you wouldn't skip oil changes, would you? Same goes for your muscles!
And don't forget about age! As we get older, muscles tend to get stiffer, so it's even more important to stay active and stretch regularly.
How Muscle Length Affects Performance
Optimal Length For Maximum Force
Okay, so picture this: your muscles are like rubber bands. If they're too stretched out or too bunched up, they won't snap with much power, right? It's the same with muscles. There's a sweet spot, an optimal length, where they can generate the most force. Think about it when you're lifting weights; you want to start in a position where your muscles can really fire.
The Impact Of Overstretching
Ever pulled a muscle? Yeah, not fun. Overstretching can seriously mess with your performance. When you push a muscle beyond its limit, you're not just risking injury; you're also reducing its ability to contract effectively. It's like pulling that rubber band too far – it loses its snap. Plus, overstretched muscles can become weaker over time. So, listen to your body and don't push it too hard!
Why Length Matters In Training
Muscle length is a big deal when it comes to training. If you're always working your muscles in a shortened position, they'll adapt and become shorter. This can limit your range of motion and your power output. That's why it's important to incorporate exercises that work your muscles through a full range of motion. Think about squats, deadlifts, and rows – these exercises help maintain and improve muscle length, which translates to better performance. Research suggests that lower limb length, alongside muscle volume, plays a significant role in muscle power production. So, keep those muscles long and strong!
The Importance Of Tension Passive In Fitness
Tension passive isn't just some fancy term for scientists; it's actually super relevant to how we move, train, and stay healthy. Let's break down why it matters in the fitness world.
Enhancing Flexibility Through Passive Tension
Think of passive tension as your body's natural resistance to stretch. It's what stops you from turning into a human pretzel! But here's the cool part: understanding and working with it can seriously boost your flexibility. By gently pushing against that resistance, you can gradually increase your range of motion. It's like convincing your muscles that it's okay to go a little further. This is especially important in activities like yoga, gymnastics, and even everyday movements. Flexibility is crucial for overall athletic efficiency.
Injury Prevention Strategies
Ever wonder why some people seem to pull muscles all the time, while others are more resilient? Passive tension plays a role. When your muscles have a healthy amount of passive tension, they're better equipped to handle sudden stresses and strains. It's like having a built-in shock absorber.
Here's how it helps:
- Improved Joint Stability: Passive tension helps stabilize joints, reducing the risk of sprains and dislocations.
- Enhanced Muscle Resilience: Muscles with good passive tension are less likely to tear or strain under stress.
- Better Movement Patterns: When muscles can lengthen and shorten properly, movement becomes more efficient and less prone to injury.
Building Strength With Proper Length
It might sound counterintuitive, but muscle length and strength are closely linked. Muscles that are too short or too long can't generate as much force. Passive tension helps maintain optimal muscle length, which is crucial for maximizing strength gains. Think of it like this: a rubber band that's stretched too tight or too loose won't snap with much power. The same goes for your muscles. By paying attention to passive tension, you can ensure that your muscles are at the right length to generate maximum force.
Proper muscle length, influenced by passive tension, allows for optimal sarcomere overlap, which is essential for force production. This balance is key to building strength effectively and safely.
Practical Applications Of Tension Passive
Incorporating Passive Tension In Workouts
Okay, so you're probably wondering how all this tension passive stuff actually helps you in the gym, right? Well, it's simpler than you think! Think about your warm-ups and cool-downs. These are prime times to focus on movements that gently stretch your muscles, allowing that passive tension to do its thing.
- Dynamic stretching before a workout can prep your muscles by increasing blood flow and improving range of motion.
- Static stretching after your workout helps to lengthen the muscles and reduce stiffness.
- Foam rolling can also be a great way to release tension in tight spots and improve flexibility.
By consciously including these types of activities, you're not just going through the motions; you're actively improving your muscle's ability to handle stress and perform better. It's like giving your muscles a little extra spring in their step!
Stretching Techniques For Better Performance
Let's talk stretching! It's not just about touching your toes (though that's a good start). Different stretching techniques can target passive tension in unique ways. For example, PNF stretching (Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation) involves contracting and relaxing muscles to achieve a greater range of motion. This can be super effective for improving flexibility and performance.
- Static Stretching: Holding a stretch for 30-60 seconds to lengthen the muscle.
- Dynamic Stretching: Controlled movements through a full range of motion.
- PNF Stretching: Contracting, relaxing, and then stretching the muscle.
Remember to listen to your body and avoid pushing yourself too hard. It's all about finding that sweet spot where you feel a good stretch without pain. Static stretching enhances the tolerance of muscles to stretching, which in turn improves joint range of motion.
Using Tension Passive In Rehabilitation
Tension passive plays a big role in rehab, especially after an injury. When you're recovering, your muscles might be tight, weak, or both. Gentle stretching and exercises that focus on lengthening the muscles can help restore range of motion and reduce pain. Think about it – if a muscle is constantly contracted, it's not going to function properly.
- Restoring Range of Motion: Gentle stretches to regain flexibility.
- Reducing Pain: Releasing tension in tight muscles can alleviate discomfort.
- Improving Muscle Function: Lengthening muscles allows them to contract more effectively.
Plus, it's not just about the physical aspect. Rehab is also about retraining your brain to control your muscles properly. By focusing on tension passive, you're helping to re-establish that mind-muscle connection and get back to doing what you love!
Common Misconceptions About Tension Passive

Debunking Myths About Muscle Stretching
Okay, so there are a ton of myths floating around about muscle stretching, and tension passive often gets caught in the crossfire. One big one? That stretching always prevents injuries. While stretching can be super beneficial, it's not a foolproof shield against getting hurt. It's more about improving your range of motion and prepping your muscles. Also, people think that if a stretch feels intense, it's automatically doing good. Not necessarily! Pain is a signal, and pushing too hard can actually cause damage. Listen to your body, folks!
Understanding Resting Tension vs. Passive Tension
This is where things can get a little confusing, even for people who are pretty into fitness. Resting tension and passive tension are not always the same thing, though the terms are sometimes used interchangeably. Think of resting tension as the baseline level of tautness in a muscle when it's at rest. Passive tension, on the other hand, is the resistance you feel when you actively stretch a muscle beyond its resting length. It's that feeling of your muscle fibers resisting being pulled. It's important to understand the difference, especially when you're thinking about how your muscles function day to day. Understanding muscle stretching is key to understanding the difference.
Clarifying Terminology In Muscle Science
Muscle science is full of jargon, and it's easy to get tripped up on the terminology. For example, people often confuse elasticity with flexibility. Elasticity is how well a muscle returns to its original shape after being stretched, while flexibility is the range of motion around a joint. They're related, but not the same. Also, the term "muscle tone" sometimes gets thrown around without a clear definition. It generally refers to the constant, low-level contraction of muscles that helps maintain posture, but it's not the same as strength or size. Getting these terms straight can really help you understand how your muscles work and how to train them effectively.
It's easy to get lost in the details, but the main thing to remember is that understanding the nuances of muscle terminology can help you make better decisions about your training and recovery. Don't be afraid to ask questions and do your research!
Future Research Directions In Muscle Mechanics
Emerging Studies On Tension Passive
It's exciting to think about where muscle mechanics research is headed! Right now, there's a lot of buzz around figuring out exactly how passive tension works at the cellular level. We're talking about diving deep into the mysteries of proteins like titin and how they contribute to a muscle's resting state. Scientists are using advanced imaging techniques to watch these tiny components in action, which is pretty cool. Understanding this better could totally change how we approach muscle injuries and rehab.
Innovations In Muscle Performance Research
Beyond the basics, researchers are also exploring how we can use this knowledge to boost muscle performance. Think about it:
- New training methods that target specific muscle fibers.
- Better ways to prevent muscle fatigue during intense exercise.
- Personalized rehab programs based on an individual's muscle mechanics.
It's not just about lifting heavier weights or running faster. It's about understanding how our muscles work so we can train smarter and stay injury-free. This could mean big changes for athletes and anyone looking to improve their physical fitness.
The Role Of Technology In Understanding Muscle Dynamics
Technology is playing a huge role in all of this. We're seeing some amazing advancements that are helping us study muscles in ways we never thought possible. For example, wearable sensors can now track muscle activity in real-time, giving us valuable data about how muscles behave during different movements. Computer models are also becoming more sophisticated, allowing us to simulate muscle function and test out new ideas before we even step into the lab. This blend of tech and science is opening up a whole new world of possibilities for muscle hypertrophy research.
Wrapping It Up
So, there you have it! Understanding how muscle length impacts muscle performance is pretty fascinating, right? It’s all about finding that sweet spot where your muscles can really shine. Whether you’re hitting the gym or just trying to stay active, knowing how to manage tension can make a big difference. Remember, it’s not just about lifting heavier weights or pushing harder; it’s about working smarter. So, take what you’ve learned here, experiment a bit, and see how your body responds. You might just unlock a whole new level of performance. Keep moving, stay curious, and enjoy the journey!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Tension Passive?
Tension Passive is the resistance that muscles provide when they are stretched. It happens because of the elastic properties of the muscle and its connective tissues.
How is Tension Passive different from Active Tension?
Active Tension is produced when muscles contract and generate force, while Tension Passive occurs when muscles are stretched without any contraction.
What factors affect muscle length?
Muscle length can be influenced by factors like genetics, training, and the types of exercises you do.
Why is the length of a muscle important for its performance?
Muscle length affects how much force a muscle can produce. Each muscle has an optimal length where it can generate the most power.
How can Tension Passive help prevent injuries?
Understanding Tension Passive can help in designing better stretching and training programs, which can reduce the risk of injuries.
What are some common myths about muscle stretching?
Many people believe that stretching always improves performance, but excessive stretching can actually weaken muscles and lead to injuries.